
When: 2022
Why: To publish images from your ip camera to Apache Server
Time: 20 minutes
Tags: Linux, RTSP, ffmpeg, Apache
What is RTSP?
The Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is an application-level network protocol designed for multiplexing and packetizing multimedia transport streams (such as interactive media, video and audio) over a suitable transport protocol.
Real time streaming protocol or RTSP is essentially the pure video and audio feed coming off IP cameras, NVRs, or networked DVRs.
1. Get your IP Camera RTSP url
The format of the string for RTSP streaming is as follows (optional components are enclosed in square brackets):
rtsp://[username[:password]@]ip_address[:rtsp_port]/server_URL[?param1=val1[¶mN=valN]] The common port for rtsp protocol are 554 and 8554.
If you need help to get your rtsp url, you can go to this page:
https://www.ispyconnect.com/cameras
Example of url cameras:
rtsp://admin:888888@192.168.0.10:8554/profile1
rtsp://rtsp:z05roG8d
@192.168.0.17:554/av_stream/ch1 Usually, the url indicates the resolution channel. In the last example profile1 and ch1 are for the low resolution channel. profile0 and ch0 are for the high resolution channel.
2. Install ffmpeg
sudo apt install ffmpegFFmpeg is the leading multimedia framework, able to decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge.
3. Install Apache
sudo apt install apache2The goal of the Apache HTTP Server project is to build a secure, efficient, and extensible HTTP server as open source, standards-compliant software. The result has long been the number one web host on the Internet.
Enable CORS headers:
sudo a2enmod headers
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.confAdd the Header in the VirtualHost tag at 000-default.conf
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*"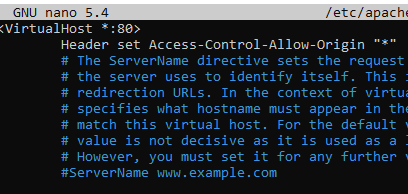
Restart apache2:
sudo systemctl restart apache24. Make a bash file to grab an image per second from the IP Camera
sudo vi /home/debian/residentfy_camera1.sh#!/bin/sh
sudo ffmpeg -rtsp_transport tcp -i "rtsp://admin:888888@192.168.0.10:8554/profile1" -r 1 -vf "scale=1024:-2" -f segment -segment_time 0.5 -segment_format singlejpeg -segment_wrap 2 /var/www/html/camera1_%d.jpg > /dev/null-rtsp_transport: Set RTSP transport protocols (Default is udp, but you can switch to tcp if you have any problems with the connection)
-i: Input file or stream
-r: Frame rate
-vf: filter_graph set video filters (In this case we scale the size of the image)
-f: Force format, in this case we will force to use segment (Demuxer)
-segment_time: Segment duration
-segment_format: Container format used for the segments
-segment_wrap: Number after which the index wraps
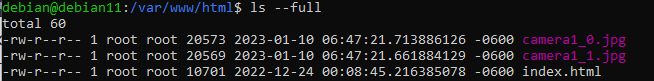
The image out will be located to the html directory from Apache. The script will create one image per second: camera1_0.jpg and camera1_1.jpg, it is neccesary to create two images to have time to read the image because is overwritten.
5. Make the file executable and test it
cd /home/debian
sudo chmod +x residentfy_camera1.sh
sudo ./residentfy_camera1.shYou can now stop the task and check for the generated images:
6. Make a Systemd Unit to control the task
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/residentfy_camera1.serviceThis is the content of the file:
[Unit]
Description=residentfy_camera1
[Service]
ExecStart=/home/debian/residentfy_camera1.sh
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable and start the unit:
sudo systemctl enable residentfy_camera1.service
sudo systemctl start residentfy_camera1.serviceCheck the status:
sudo systemctl status residentfy_camera1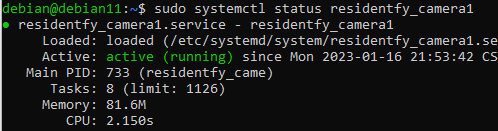
7. Make a bash file to “monitor” the task, because the task could stop if there is a intermitent net connection.
sudo nano /home/debian/residentfy_monitor.shThis is the content of the file:
#!/bin/sh
while true
do
MODIFICADOS=$(find /var/www/html/camera1*.jpg -mmin -5 -type f -ls | wc -l)
if [ "$MODIFICADOS" -eq "0" ]; then
echo "NO HAY ARCHIVOS MODIFICADOS CAMARA 1. REINICIANDO";
sudo systemctl restart residentfy_camera1
fi
#REINICIAMOS EL SERVICIO TODOS LOS DIAS
HORA=$(date +"%H%M")
#DIFERENCIA DE 5 MINUTOS, IGUAL QUE EL SLEEP
if [ "$HORA" -ge 2353 ] && [ "$HORA" -le 2358 ]; then
echo "REINICIAR"
sudo systemctl restart residentfy_camera1
sleep 1m
fi
sleep 5m
doneThe bash file check if the images has been modified in the last 5 minutes. If not, restart the task.
Give permission of execution:
sudo chmod +x /home/debian/residentfy_monitor.shCreate the unit file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/residentfy_monitor.serviceThis is the content of the file:
[Unit]
Description=residentfy_monitor
[Service]
ExecStart=/home/debian/residentfy_monitor.sh
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetEnable and start the service:
sudo systemctl enable residentfy_monitor.service
sudo systemctl start residentfy_monitor.service