
When: 2022
Why: You need a fully functional Linux server on a Windows Machine (And need to do it fast)
Time: 20 minutes
Tags: Linux, Virtualbox
What is VirtualBox?
VirtualBox is a powerful x86 and AMD64/Intel64 virtualization product for enterprise as well as home use. Not only is VirtualBox an extremely feature rich, high performance product for enterprise customers, it is also the only professional solution that is freely available as Open Source Software under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) version 3.
Presently, VirtualBox runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, and Solaris hosts and supports a large number of guest operating systems including but not limited to Windows (NT 4.0, 2000, XP, Server 2003, Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10), DOS/Windows 3.x, Linux (2.4, 2.6, 3.x and 4.x), Solaris and OpenSolaris, OS/2, and OpenBSD.
1. Download and install VirtualBox for Windows from the page:
https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
2. Maybe you will need to install Visual C++ redistributable package:
https://learn.microsoft.com/es-es/cpp/windows/latest-supported-vc-redist?view=msvc-170
3. Download a VirtualBox Linux image:
https://www.linuxvmimages.com/images/debian-11/
4. Open the VirtualBox file
Just unzip the file that you download and open the VirtualBox file.
When you start the VirtualBox, you will see something like this:

The image i downloaded was Debian 11 (Minimal). The user and password are “debian”. The IP asigned was 10.0.2.15, because the Virtual Machine is behind a NAT Network. If you want to expose some ports to other machine on the network, just configure a port forwarding:
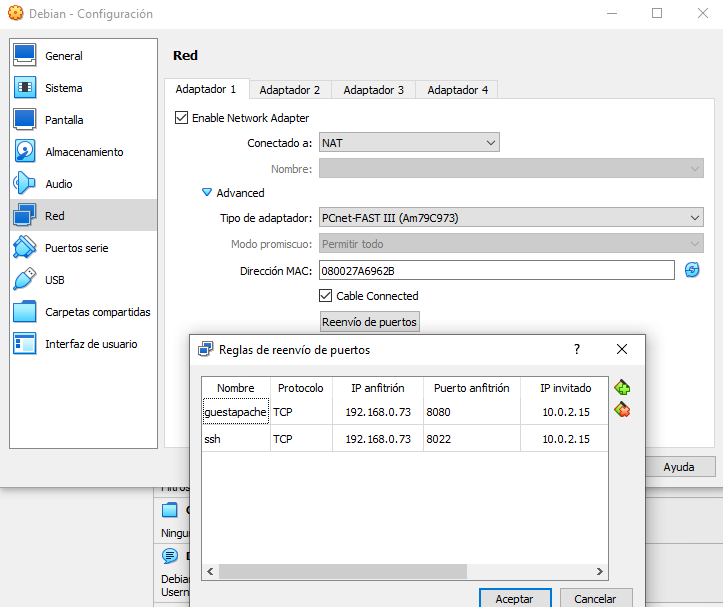
In this example, the host machine (Windows) has the IP 192.168.0.73. If you have any problems, you can try disabling the firewall or antivirus software.
Adapter Type: Paravirtualized Network